Understanding the Demand Model
Tired of updating demand one at a time? Do you want to quickly construct a fiber allocation model based on address type? This article explains how to use the Demand Model to get your fiber allocations right quickly and accurately.
Overview
The Demand Model allows you to quickly and consistently allocate fiber service to locations based on Address Type.
The Demand Model will only be available for Architectures & Projects created after the 12th of September, 2023.
Finding the Demand Model
The Demand Model can be access via the Architecture Configuration Panel and is configured directly after your network architecture settings.
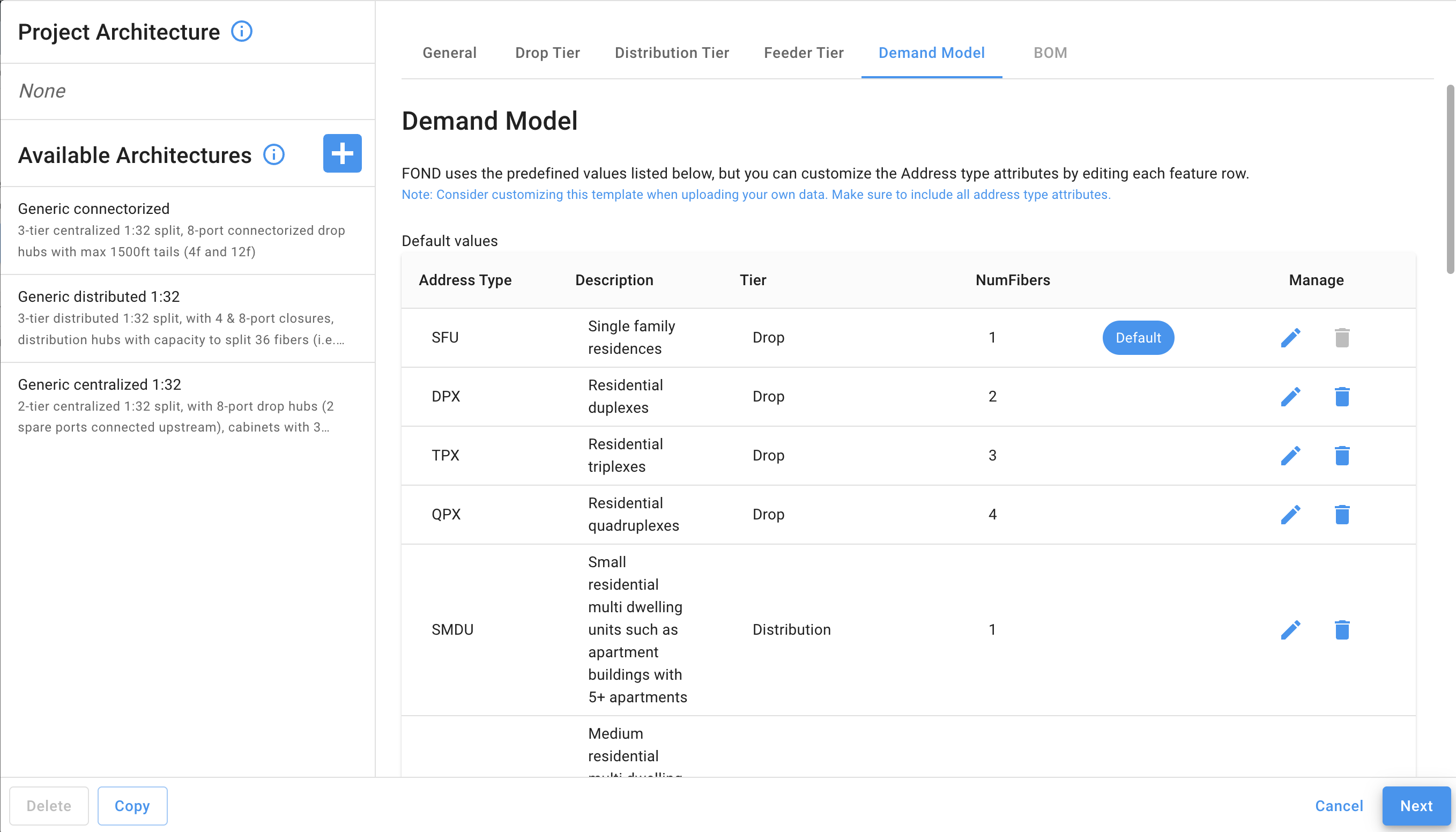
Understanding the Demand Model Controls
The Demand Model allows the ability to create and update fiber allocations to new or existing address types respectively. To do this successfully, there are a number of controls available, which can be seen below:
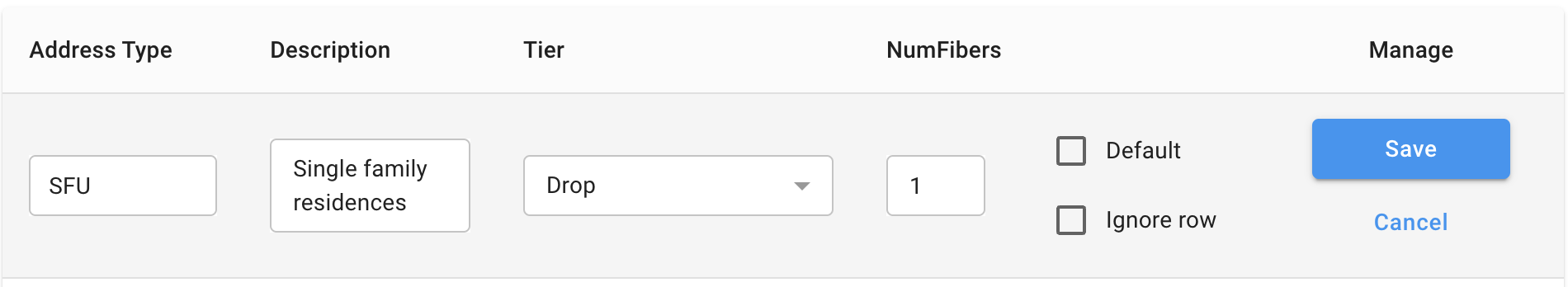
Address Type
The classification to be found in your "AddressType" field. By setting this value, "all addresses with the Address Type will have the described fibers allocated".
Description
Don't forget the type of address by providing a short summary of the addresses this Fiber Allocation Standard should be applied to.
Tier
The tier of the network (Drop, Distribution, Feeder) that the fibers should be allocated from. As a general rule, larger addresses should be served from further up the network.
NumFibers
The number of fibers that should be provided to this address. As a general rule larger, higher bandwidth addresses should have more fibers allocated. This should be an integer greater than or equal to zero.
Setting NumFibers to zero will result in the address being unserved. These addresses will not be billed
Default
By selecting this option, this Fiber Allocation should be used as the Standard and applied to any Addresses which don't have an Address Type in the Demand Model. For example, if an Address is uploaded with Address Type: "Gas Station" and there is no "Gas Station" fiber allocation in the demand model, it will be assigned the default value.
Default Address Types cannot be deleted.
You may only have one default address type
Ignore Row
By selecting this option, the address will not be considered in the Project.
The design will not include this address and therefore the address will not be billed.
Updating Existing Demand Model Items
The demand model allows you to not only see your current Fiber Allocations, but also manage how they work.
Ensuring all Demand is Modeled
If there is an address which has an 'Address Type' value that isn't in the Demand Model, FOND will notify you of the Type that is not included. Any Address that has an unsupported Address Type will have the Default Demand Model Allocated.
If this is not the desired behavior, a new Fiber Allocation item should be added to the Demand Model.
The Standard Model
Not sure where to start? Not a problem! FOND comes with a standard Demand Model, which you can build on to fit your needs. There are two components to FOND's Standard Demand Model: Standard Fiber Allocation Model & Pre-classified Addresses.
Standard Fiber Allocation Model
The standard model is available under the Demand Model panel, when a new Architecture is created.
| Address Type | Serve | Tier | NumFibers |
| SFU | True | Drop | 1 |
| DPX | True | Drop | 2 |
| TPX | True | Drop | 3 |
| QPX | True | Drop | 4 |
| SMDU | True | Distribution | 1 |
| MMDU | True | Distribution | 2 |
| LMDU | True | Feeder | 2 |
| SCU | True | Drop | 1 |
| MCU | True | Distribution | 1 |
| LCU | True | Feeder | 1 |
| INSTITUTION | True | Feeder | 1 |
| GOVT | True | Distribution | 1 |
| PUBLIC | True | Drop | 1 |
| DNS | True | N/A | N/A |
Pre-Classified Addresses
The fastest way to apply the Standard Demand Model is by using the Pre-classified Addresses. FOND has addresses which have been classified ahead of time which are accessible through the Area Select capability. When you Area Select Addresses, you will see a column titled: "Address Types" which will contain an Address Type from the above table.
The Addresses have been classified primarily around their "LandUse" field, providing a standardized classification based on the type of location which was found at that location.
| Address Type | Description | Examples |
| SFU | Single Family Residences | Single Family Homes |
| DPX | Residential Duplex | Two Family Residences |
| TPX | Residential Triplex | Three Family Residences |
| QPX | Residential Quadplex | Four Family Residences |
| SMDU |
Small Residential Multi Dwelling Unit (5-10 addresses) |
Apartment Buildings |
| MMDU |
Medium Residential Multi Dwelling Unit (10-100 addresses) |
Apartment Buildings |
| LMDU |
Medium Residential Multi Dwelling Unit (100+ addresses) |
Apartment Buildings |
| SCU | Small Commercial Unit | Retail Stores, Offices, Farms, etc. |
| MCU | Medium Commercial Unit | Office Buildings, Department Stores, Neighborhood Shopping Centers, Hotels, Medical Clinics, etc |
| LCU | Large Commercial Unit | Shopping Malls, Multi-storey Office Buildings, Arenas, etc |
| INSTITUTION | Various High Bandwidth Facilities | Schools, colleges, hospitals, museums, places of worship, etc |
| GOVT | Government Offices & Facilities | Government administration offices, military locations, public health care facilities, etc |
| PUBLIC | Public Buildings | Community centers, Municipal Facilities, etc |
| DNS | "Do Not Serve" - Addresses which should not be serviced by the network. | Unspecified, Vacant, Exempt, Forest, etc. |