Sourcing data with Area Select
This guide will go through how you can source Address and Street Centerline data for your project using FOND's Area Select feature.
What is Area Select?
The idea behind Area Select is to provide users with base data to get their project going. Using Area Select allows you to draw or upload a polygon and obtain key input data from within that polygon, provided that we have the data available within our database.
Area Select is able to provide you with Street Centerlines for anywhere in the USA or Canada, as well as Address data that has been derived from land parcel data for US counties and populous areas of Canada. Our Street Centerline data is imported into FOND as underground path.
In most cases, the quality of Street and Address data is available through Area Select is adequate for a Feasibility Design. If you're doing High-Level Designs or Low-Level (Detailed) Designs, you may want to use FOND's drawing tools (underground, addresses) to touch up the data to make it more accurate and appropriate for construction.
Using Area Select
Drawing a polygon
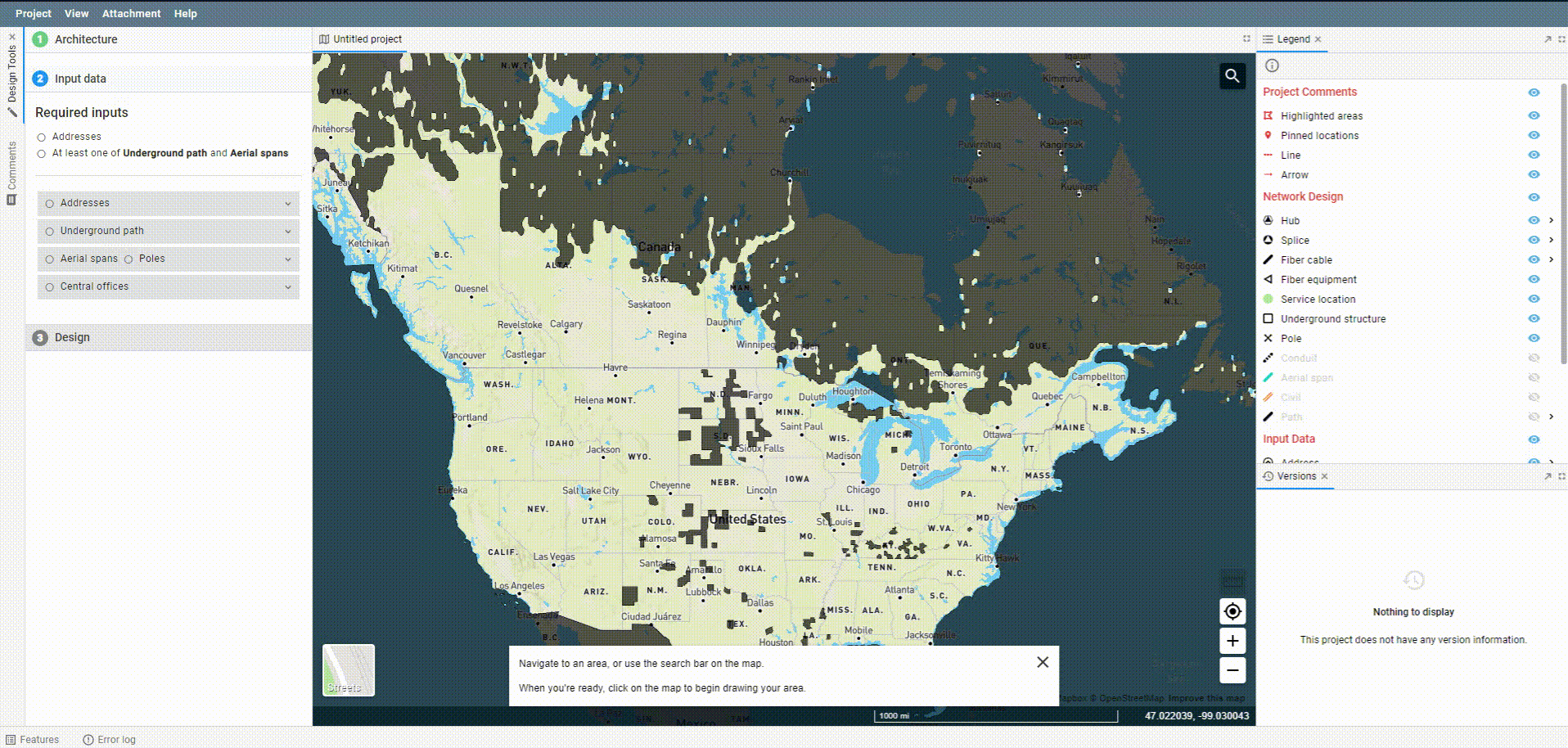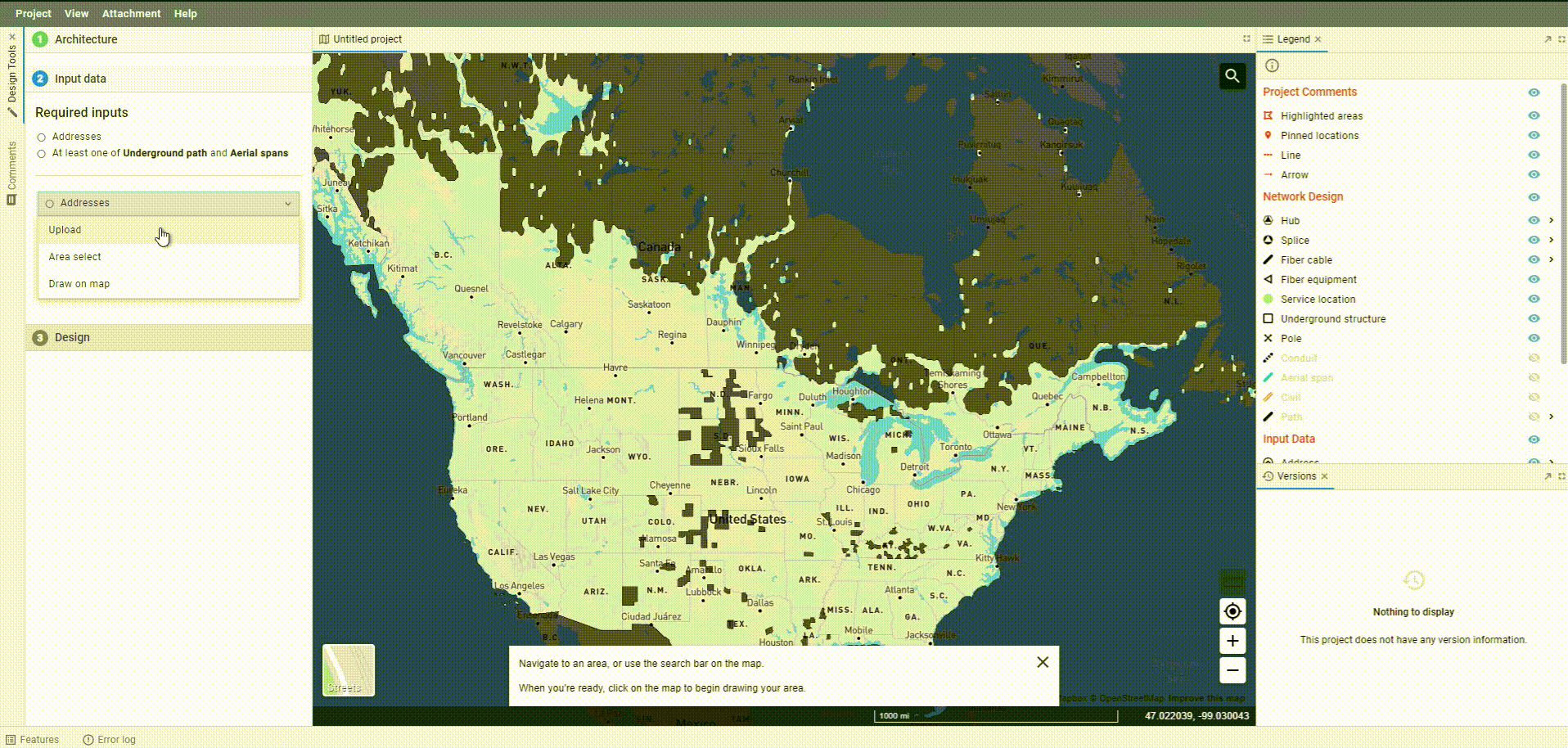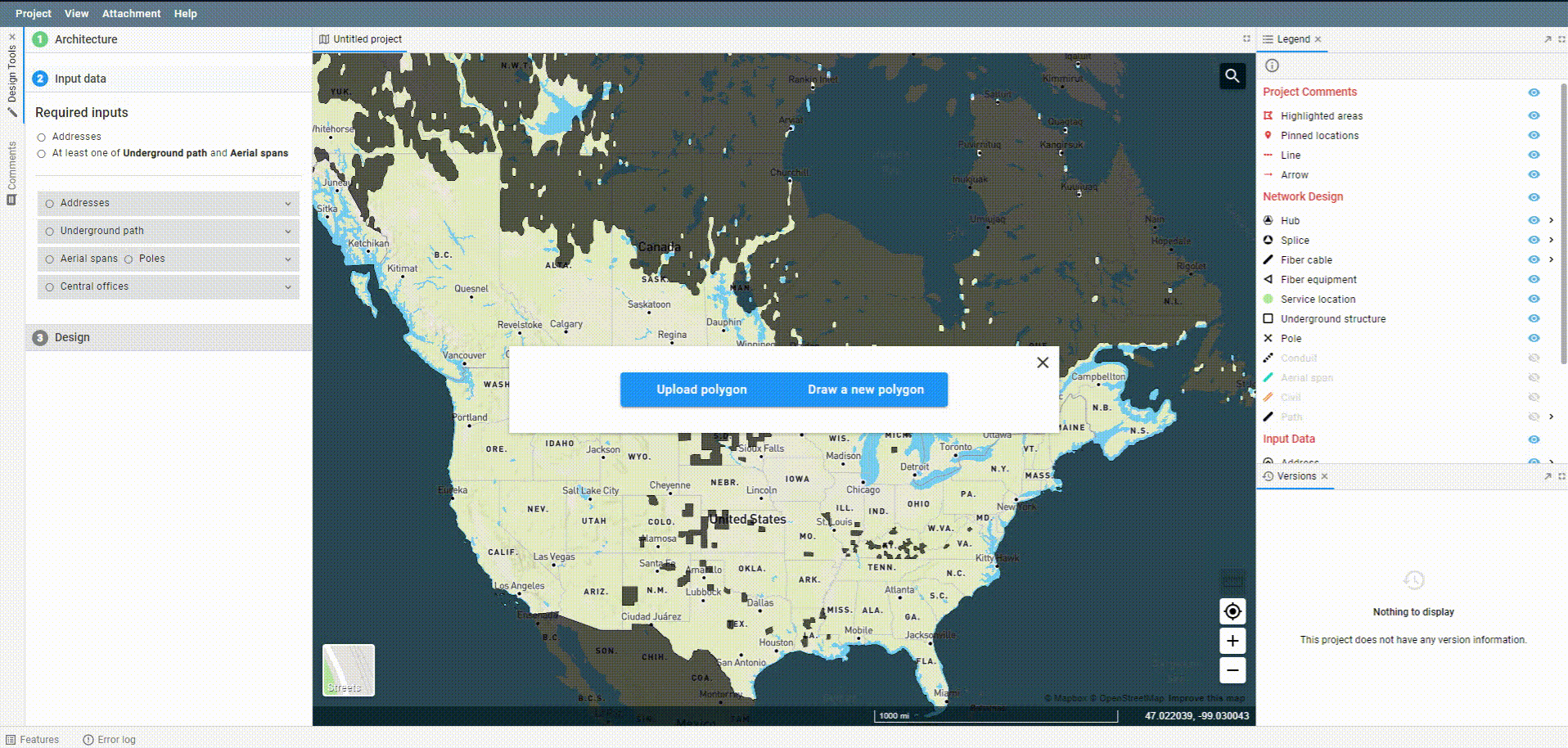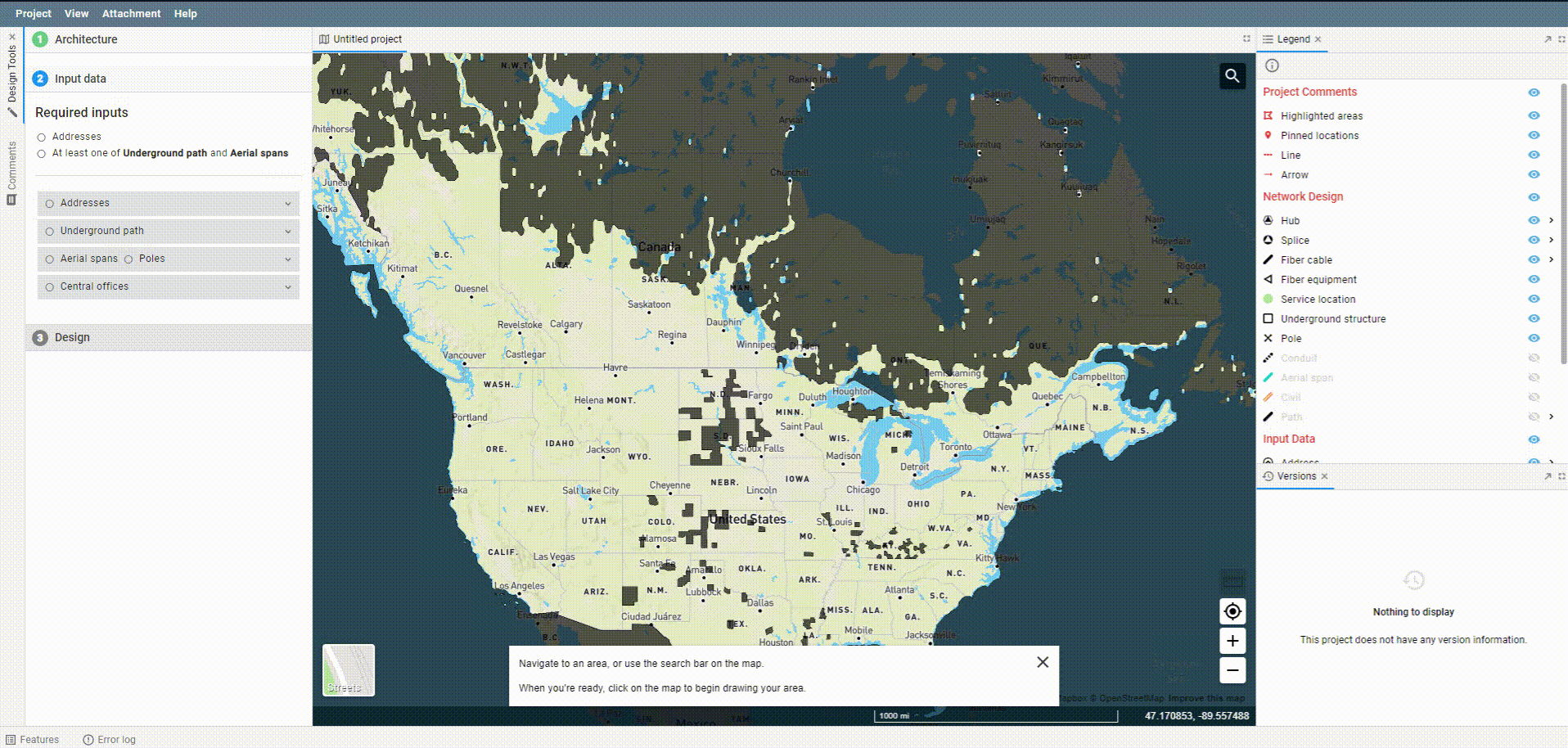
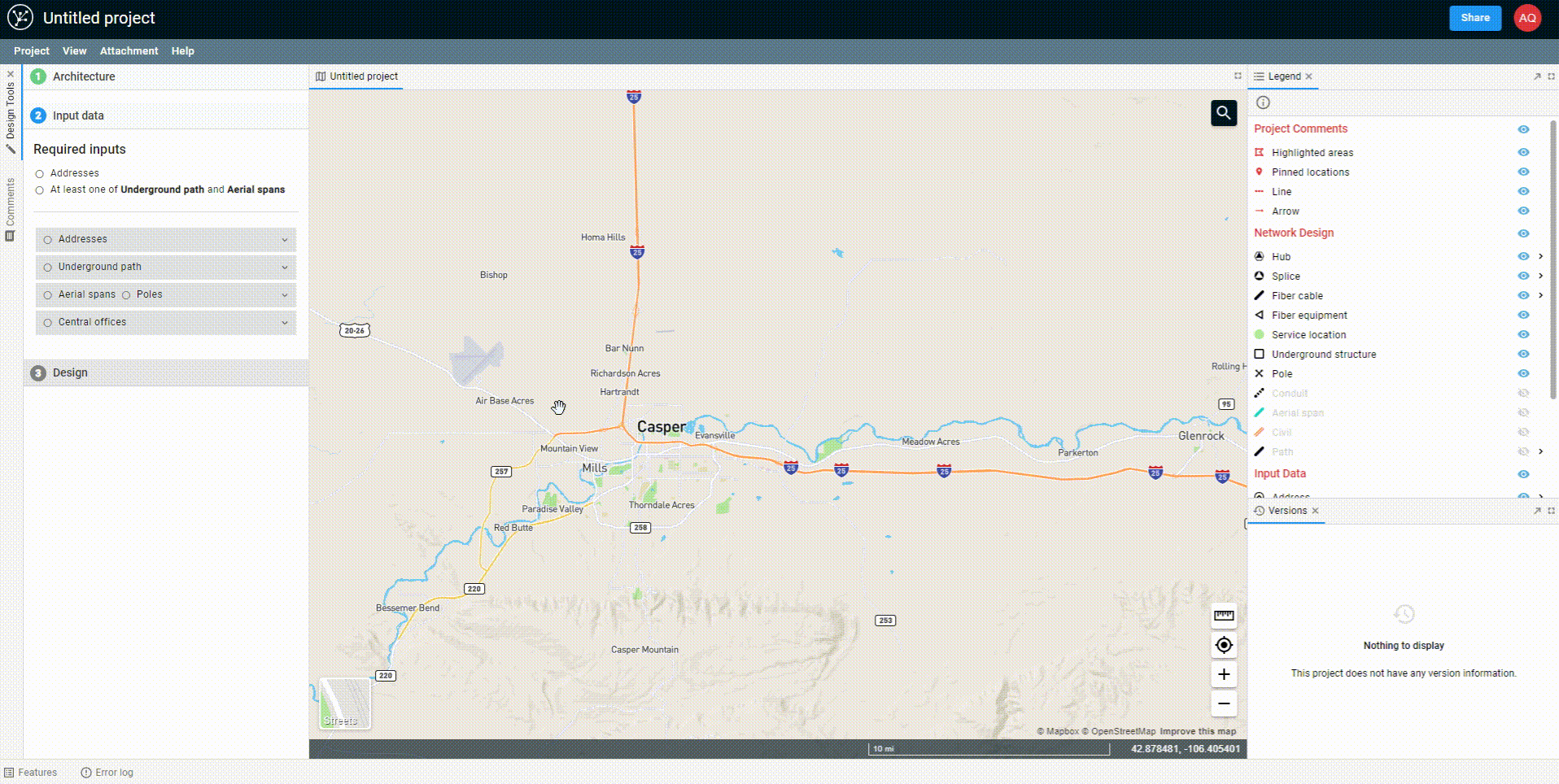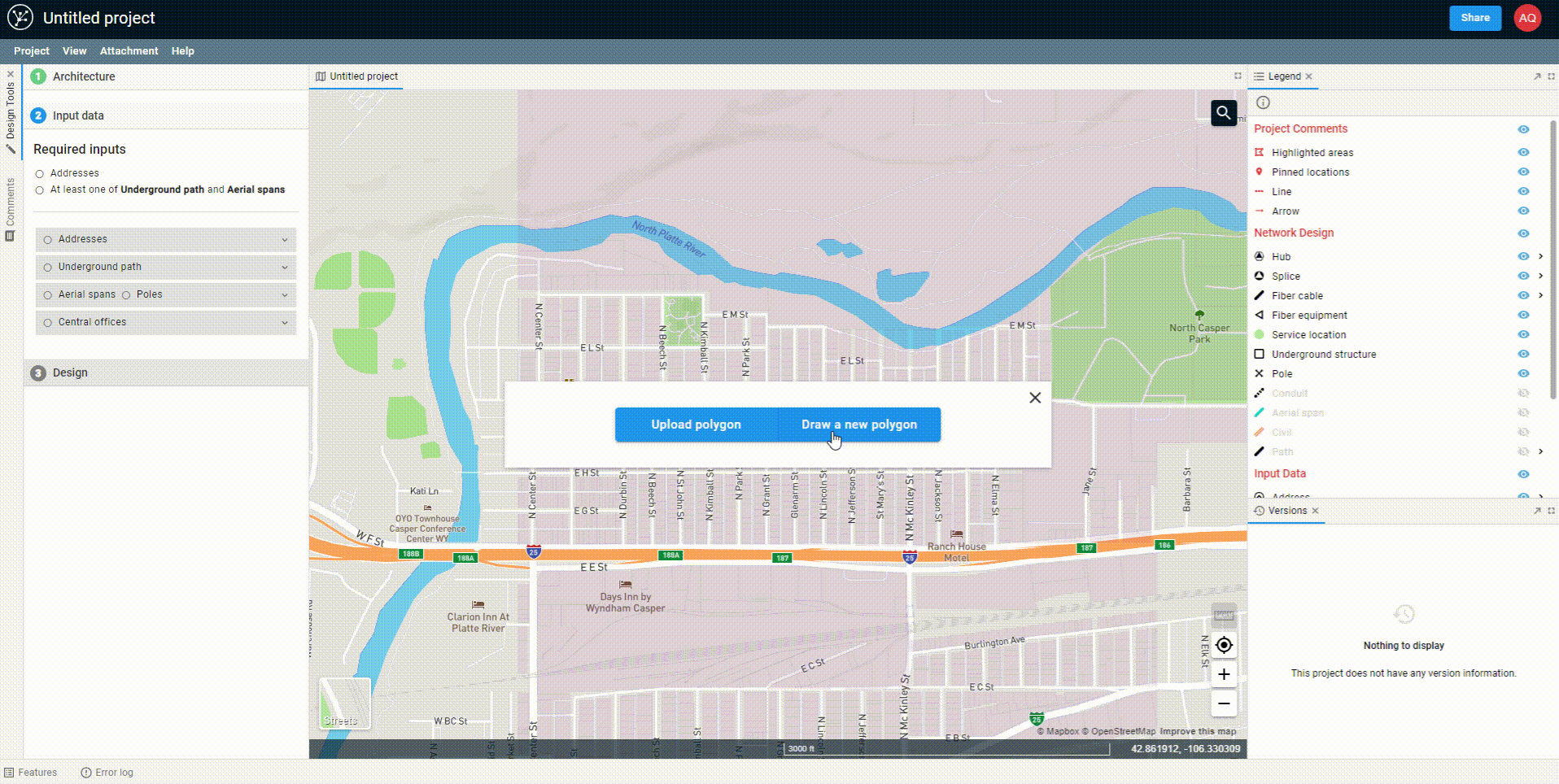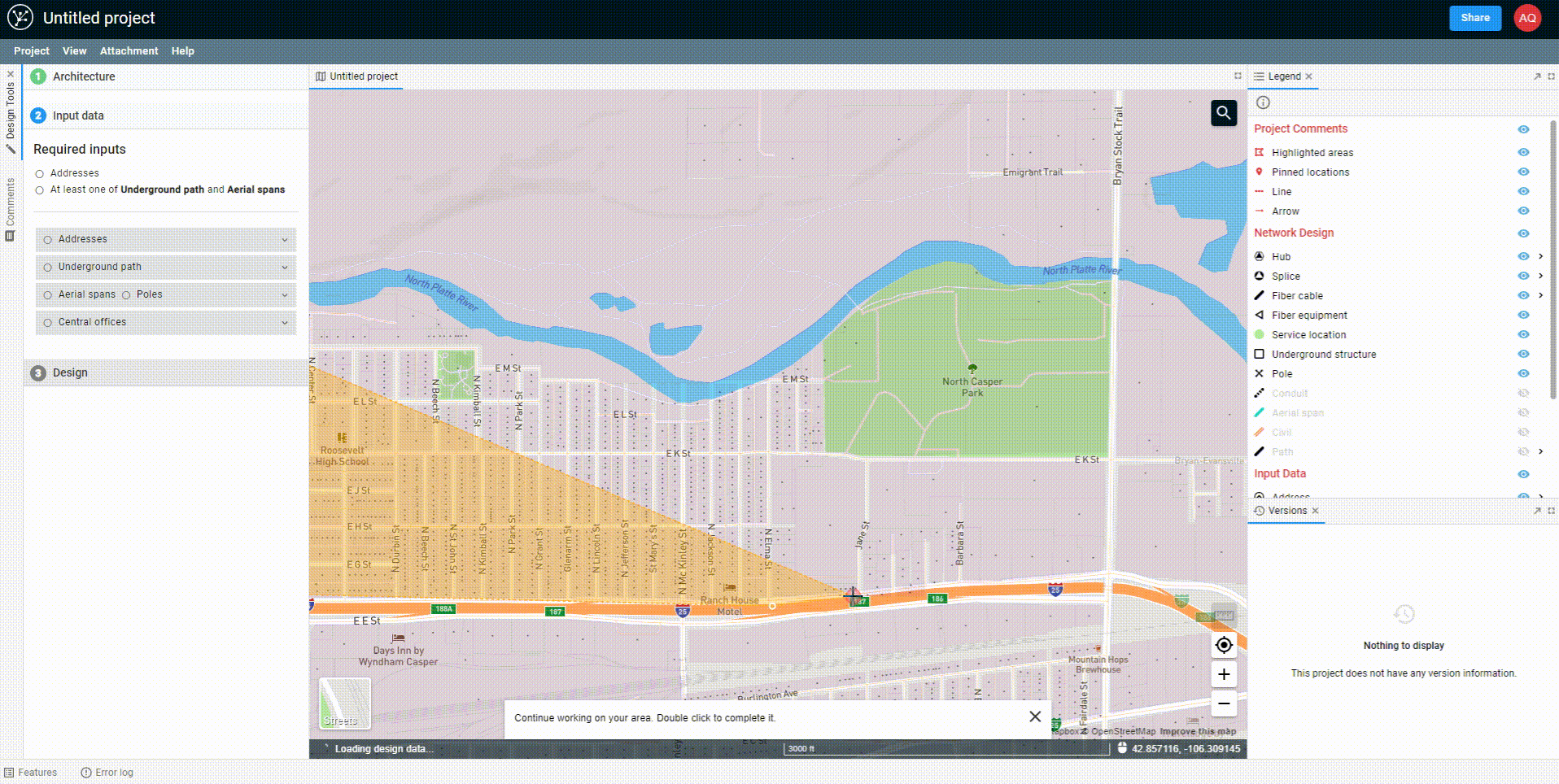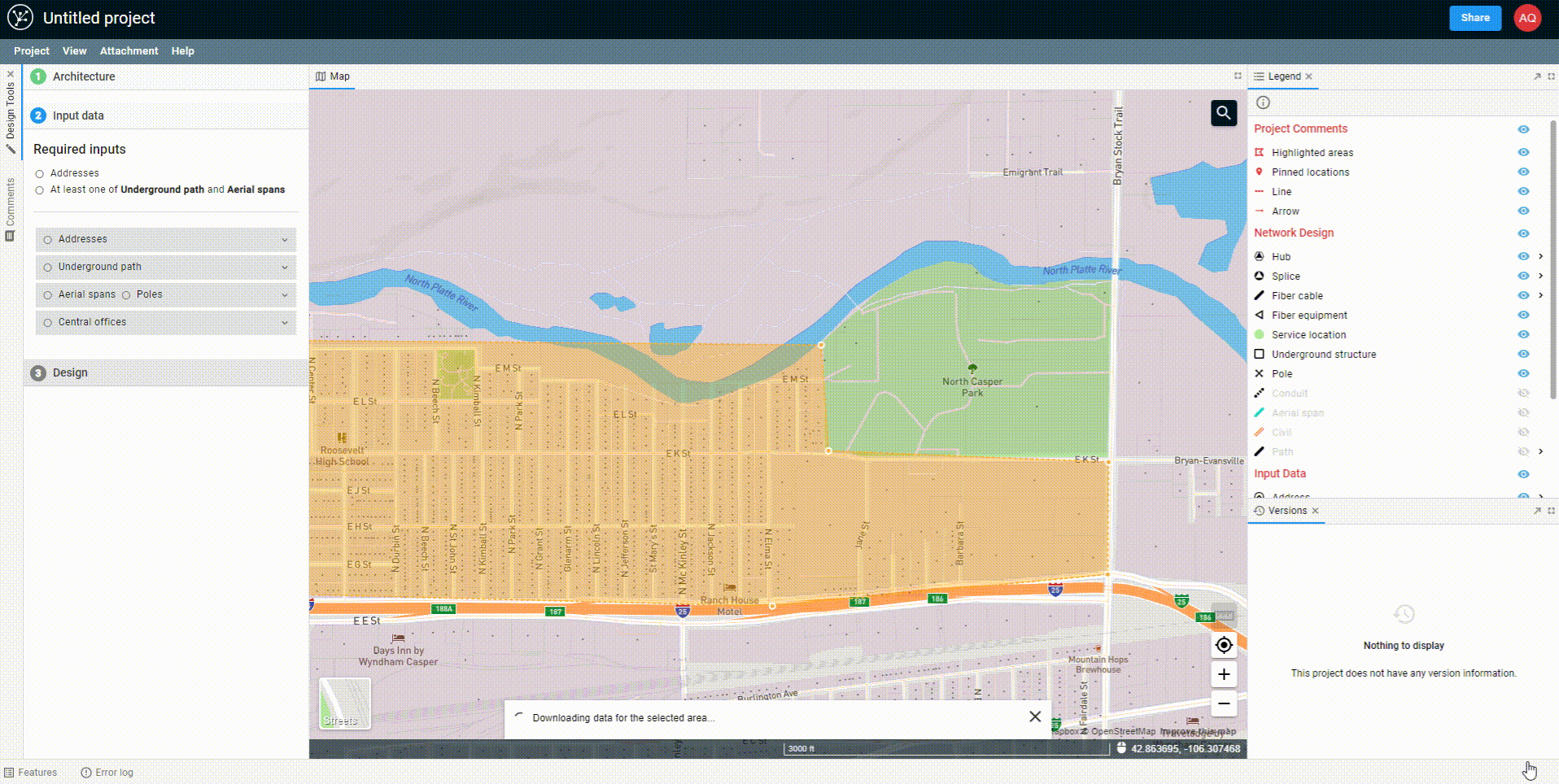
Open up the feature by choosing the Area Select option from Address or Underground path in the Input data section of FOND. Then, choose to draw a new polygon.
You'll see the map of the USA mostly lit up, as well as much of Canada. The light sections of the map have both addresses and street centerlines. Dark sections in the USA and Canada have only street centerlines.
As you zoom into the map, the data within our database will become visible on screen. First, land parcel data appears. As you get closer, you can view addresses and street centerlines too. This allows you to be precise when drawing your polygon boundary, so that you only select the places where you want to download data.
Begin drawing a polygon by clicking on the map. Continue to click in each location where you would like to create a vertex. To complete the polygon, either double-click on the map or hit Enter on your keyboard.
Navigating the map
There are two ways to navigate to the area that you'd like to source data for.
The first option is to zoom in to the area of the map you're interested in with the map tools (this guide on moving around the map is relevant).
In the GIF above, we zoom in with the scrollbar of the mouse. Note, once you're in area select mode, clicking on the map will begin drawing on the map. However, clicking and dragging will still allow you to pan on the map). Once you're in place, you can begin drawing your polygon.
The second option for moving around the map in Area Select mode is to use the geocoder search bar. Once you're where you need to be, the steps are all the same as above.
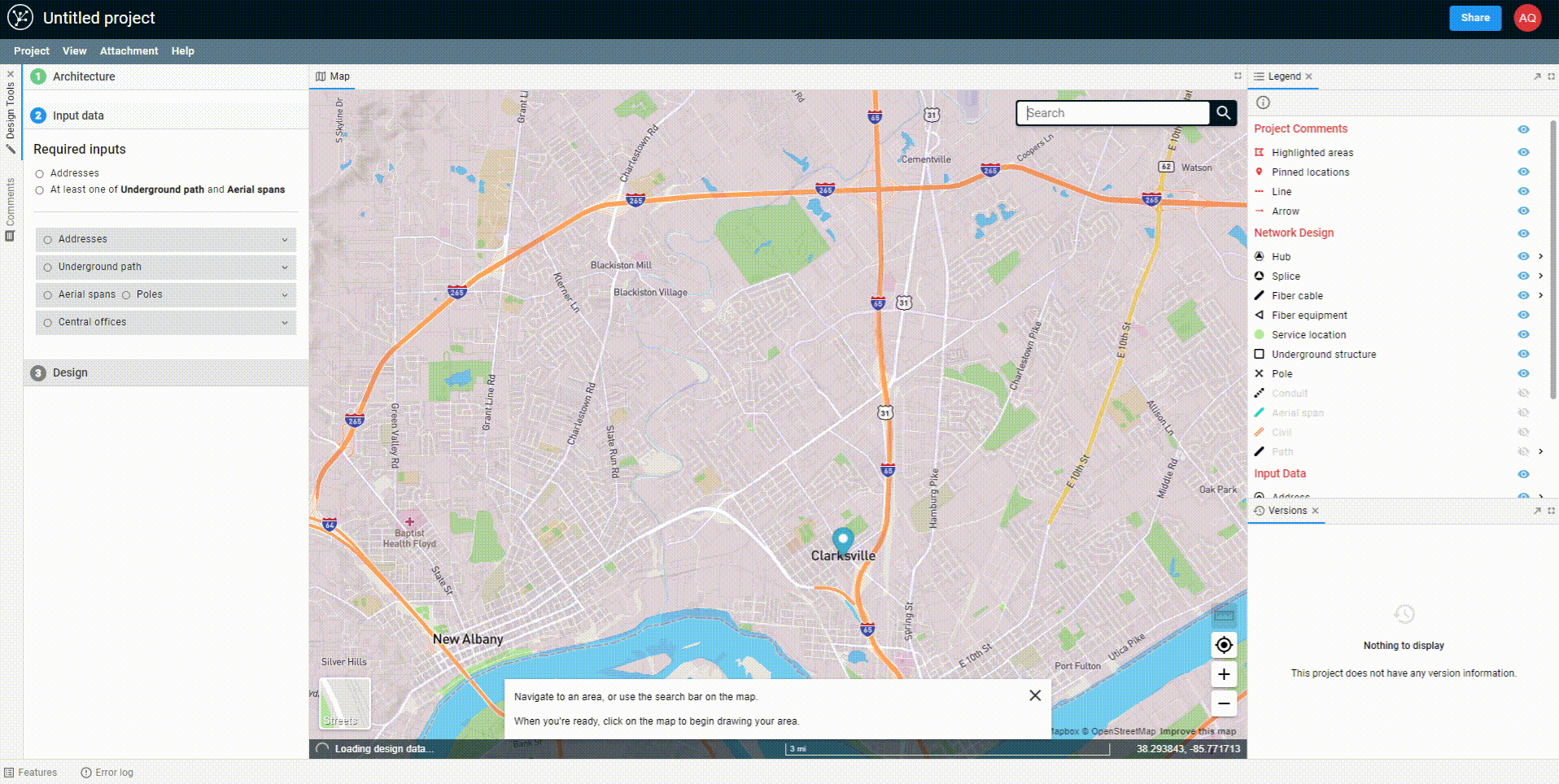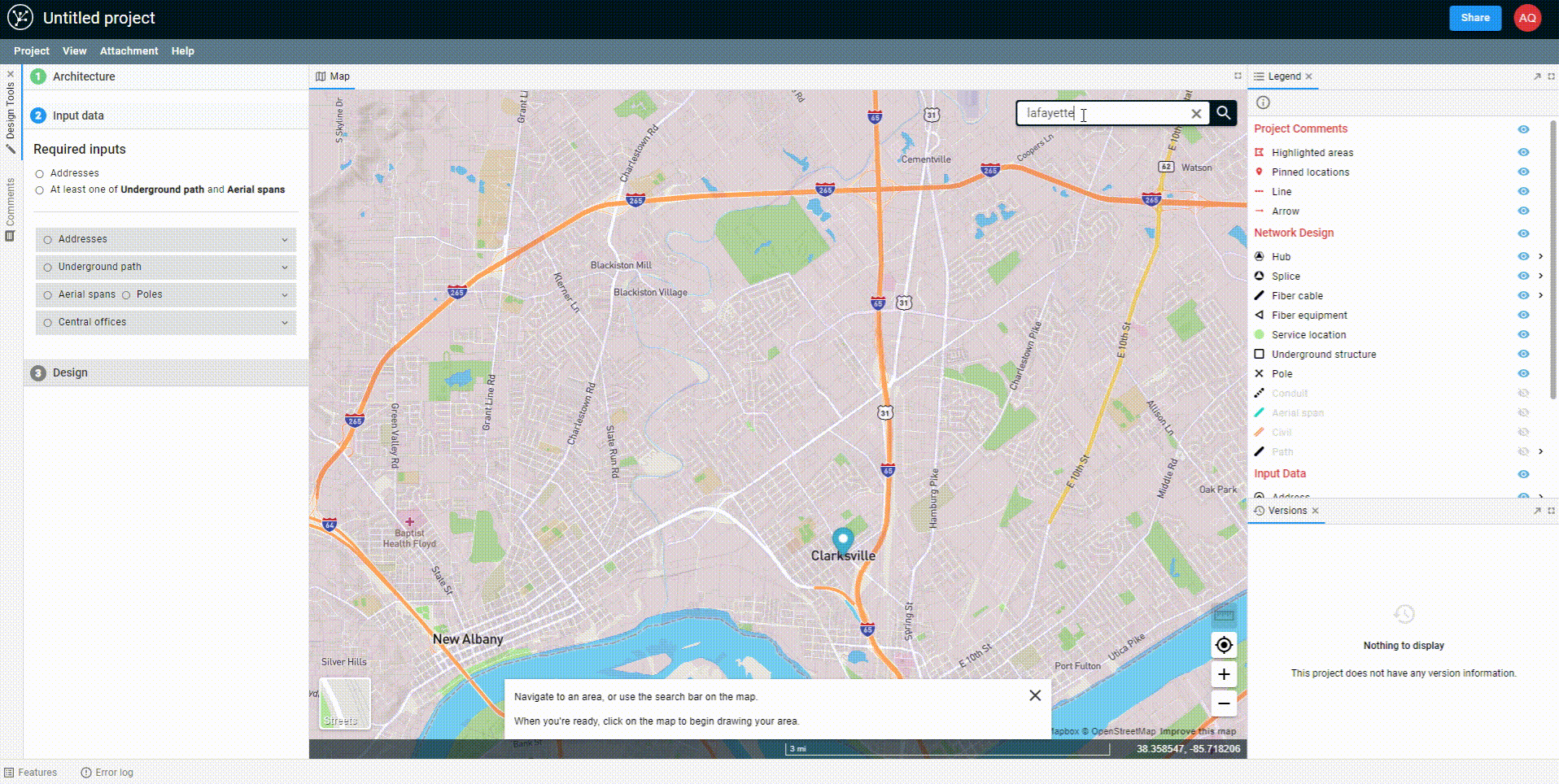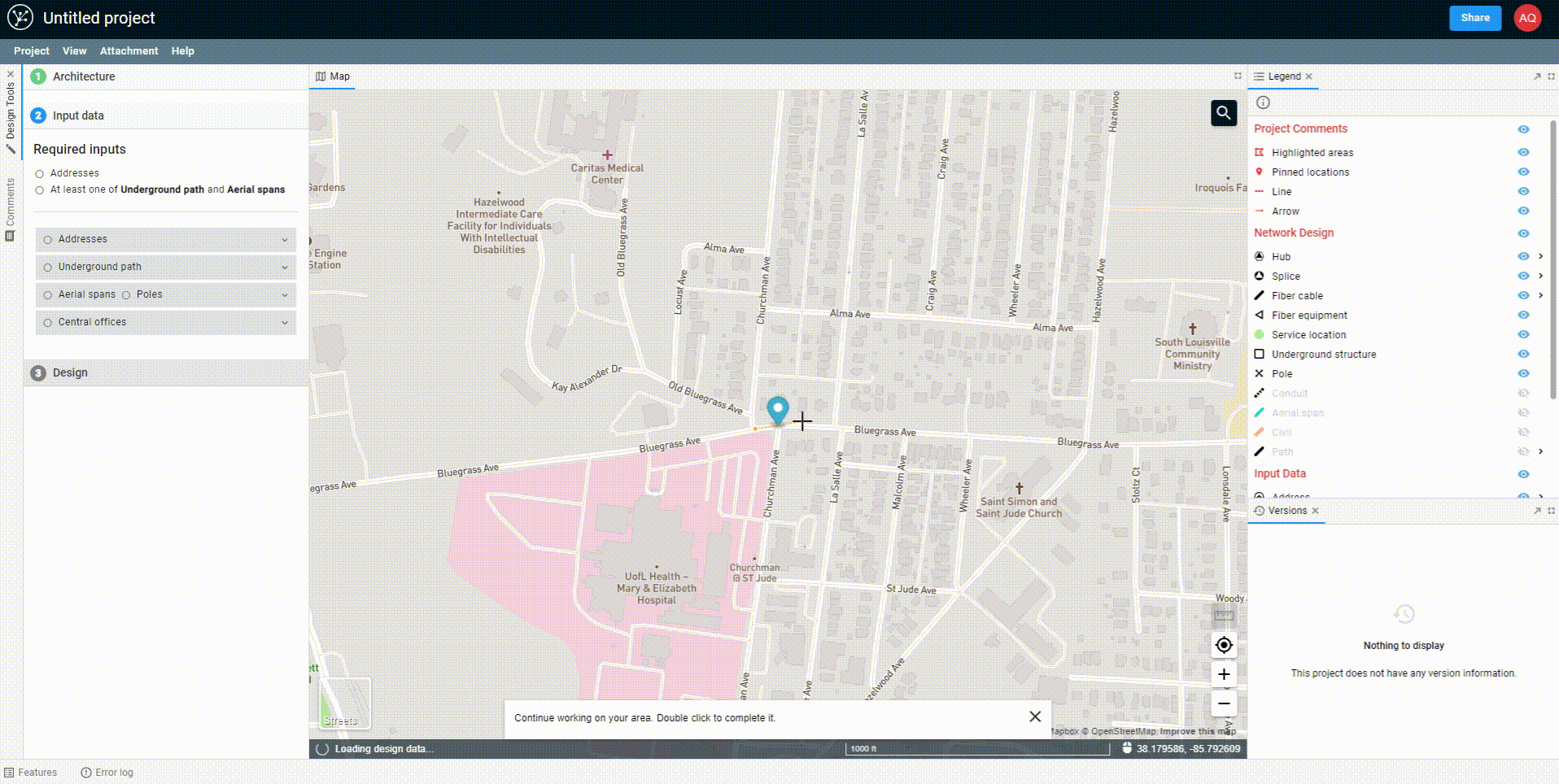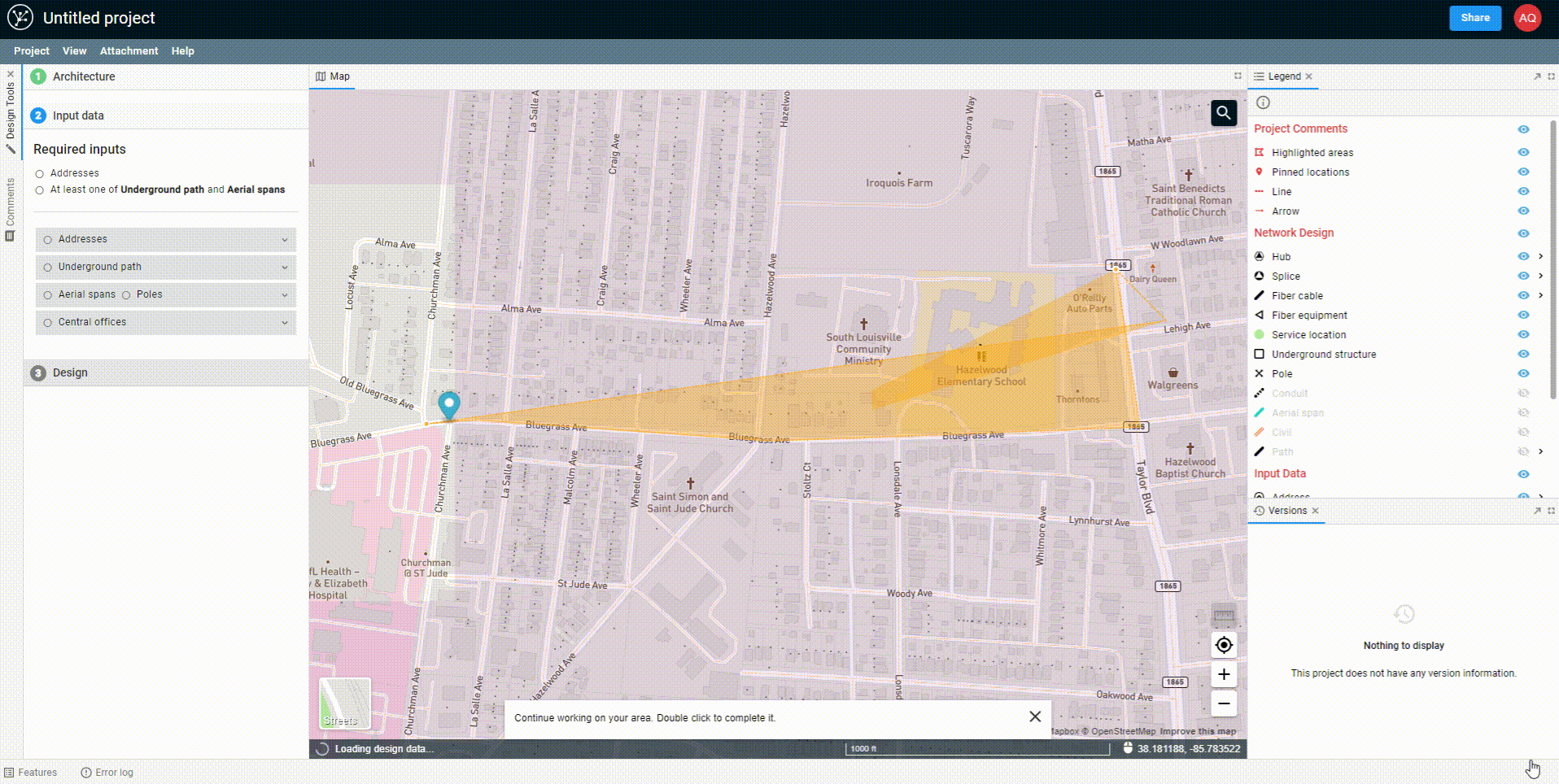
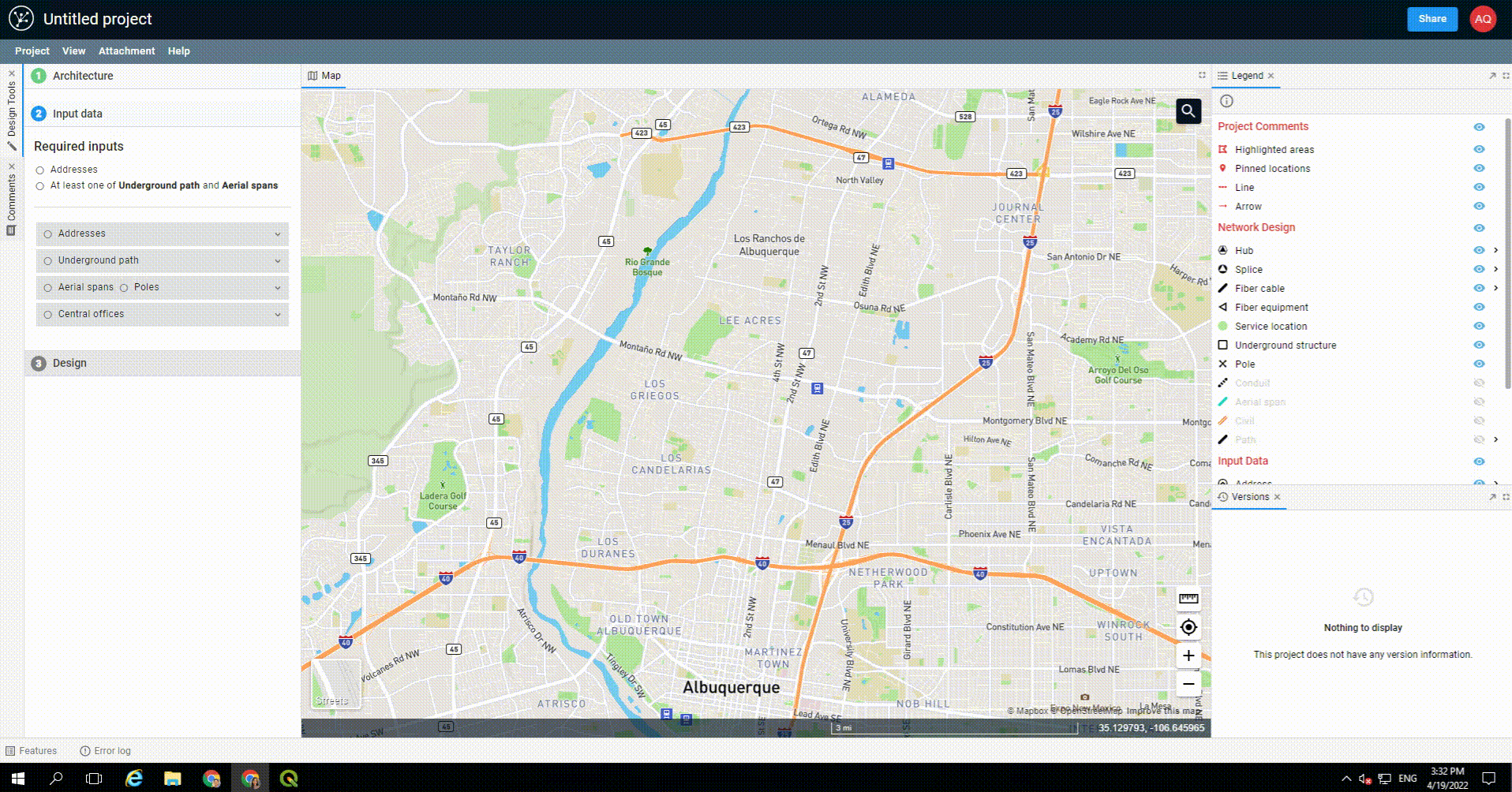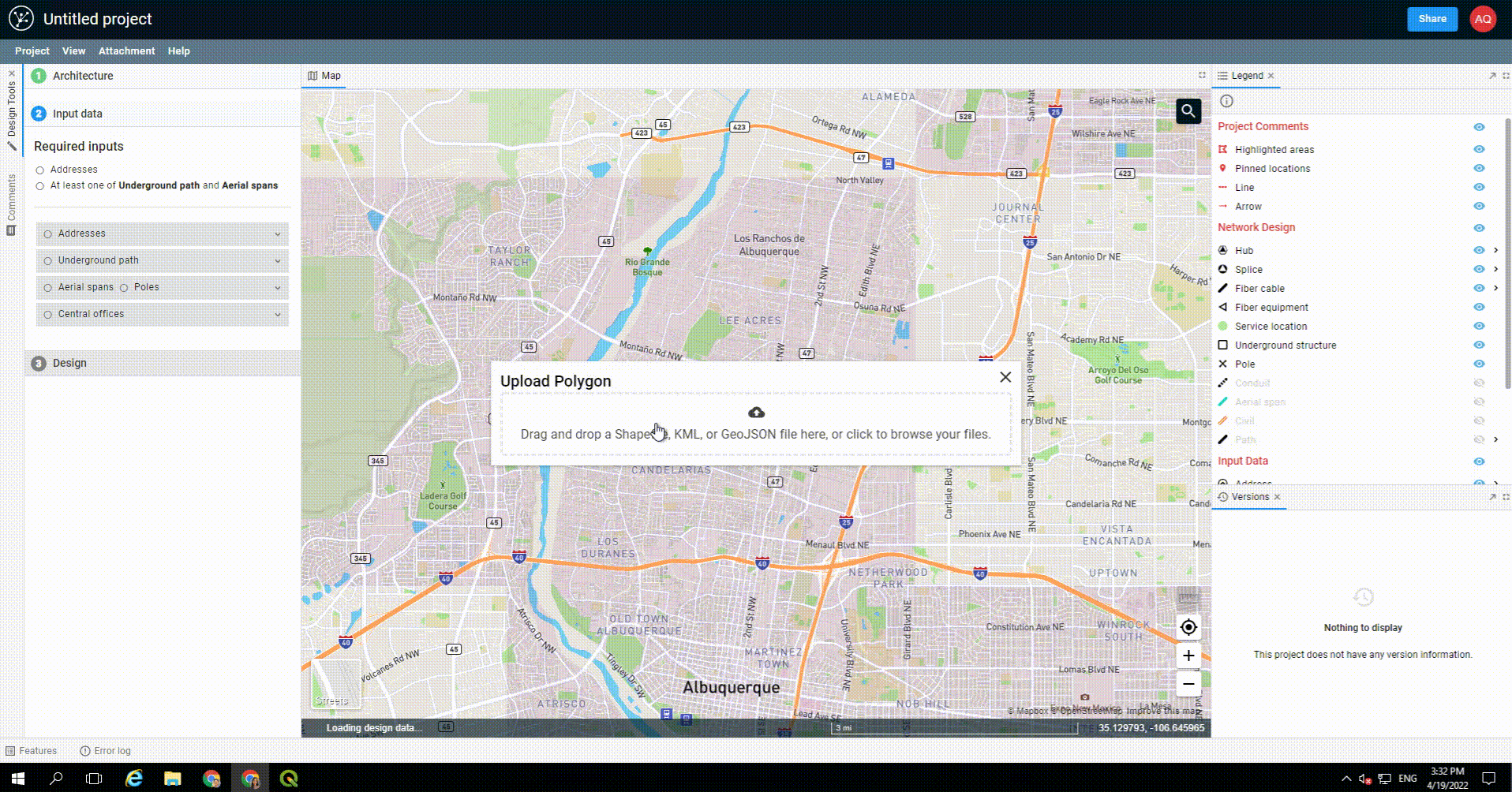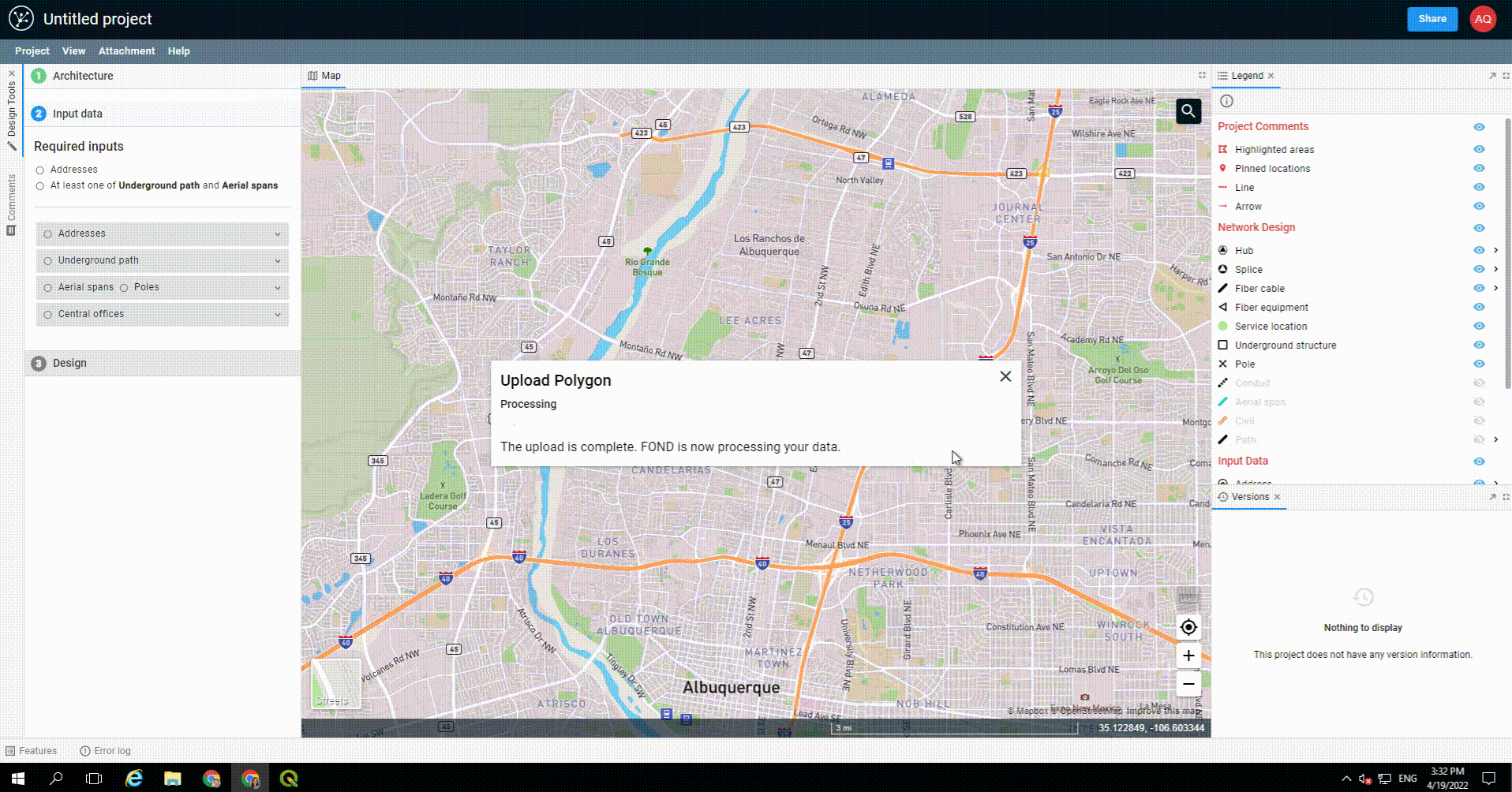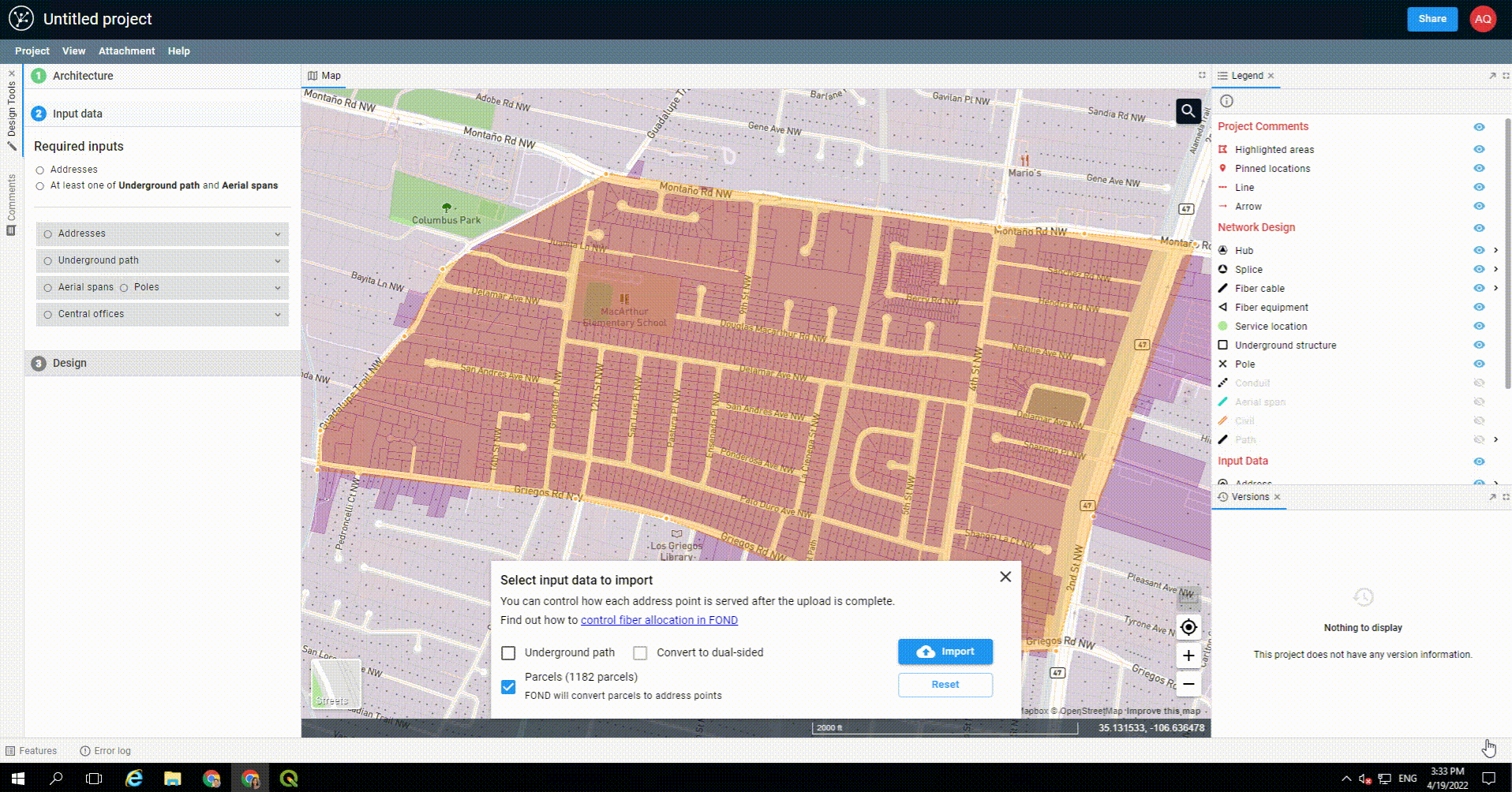
Once you've drawn the polygon, the data will begin to come down out of the FOND database, and you'll see options for both the underground path and parcels. You can select one or both of these to import into your project.
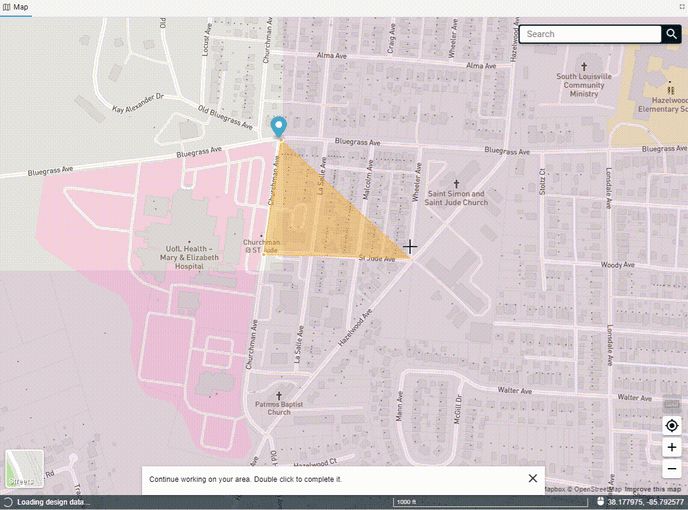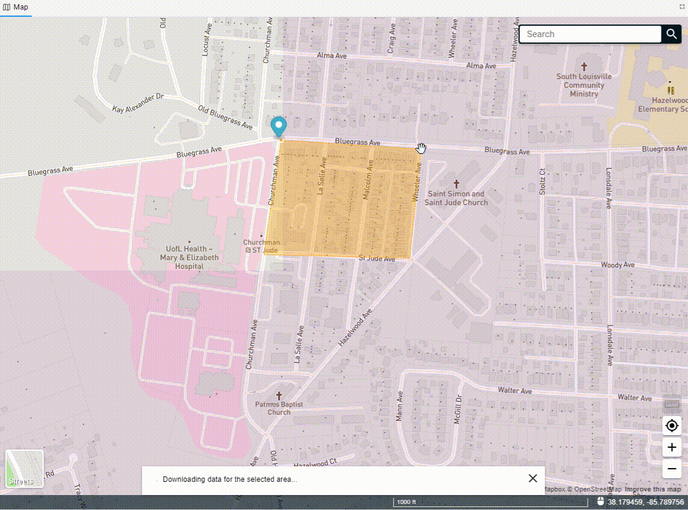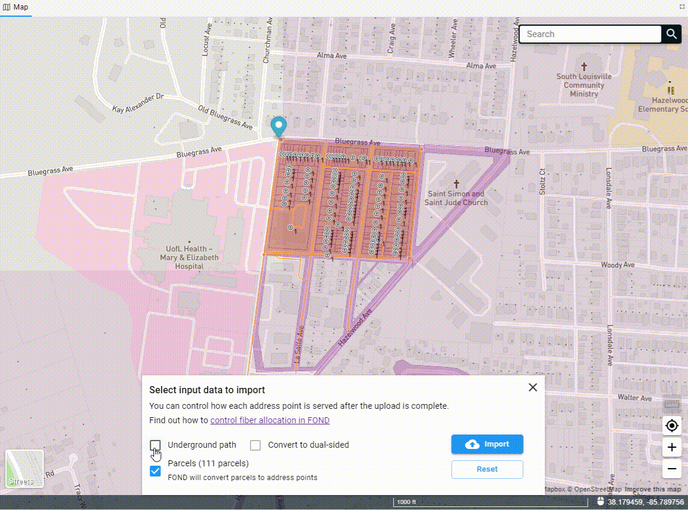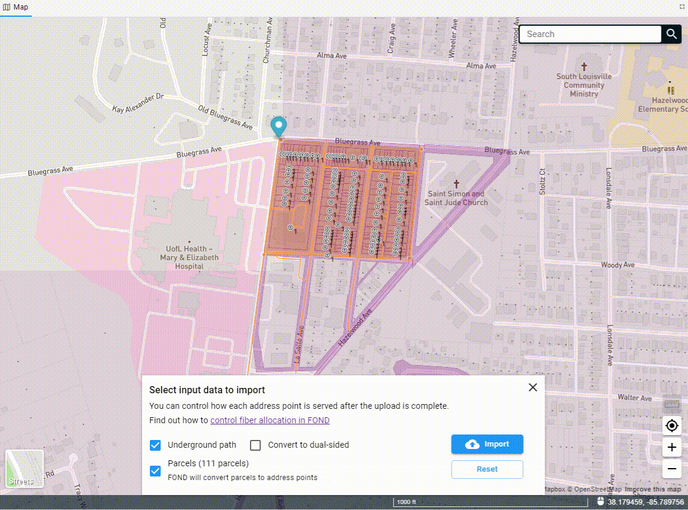
You can also edit the polygon after you've drawn it by adding more vertices to the edge of the polygon and dragging them. You may need to click on the polygon to 'activate' it first.
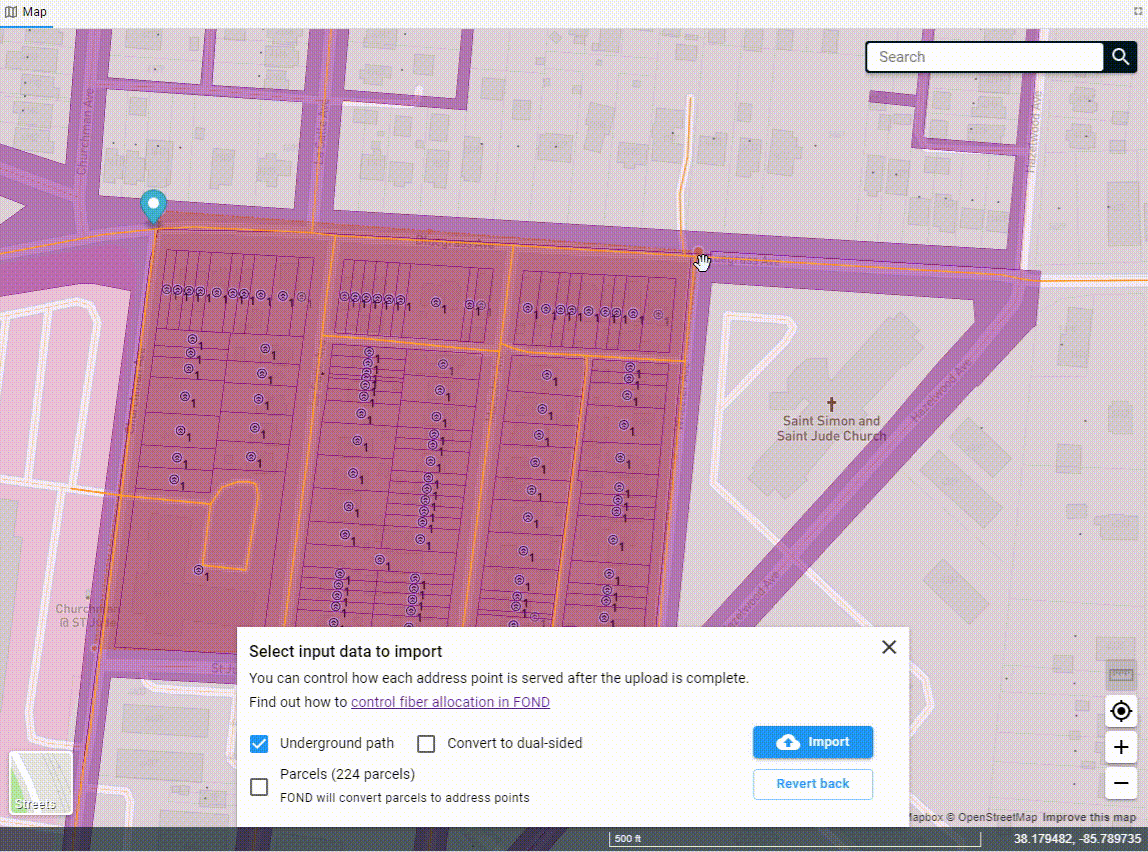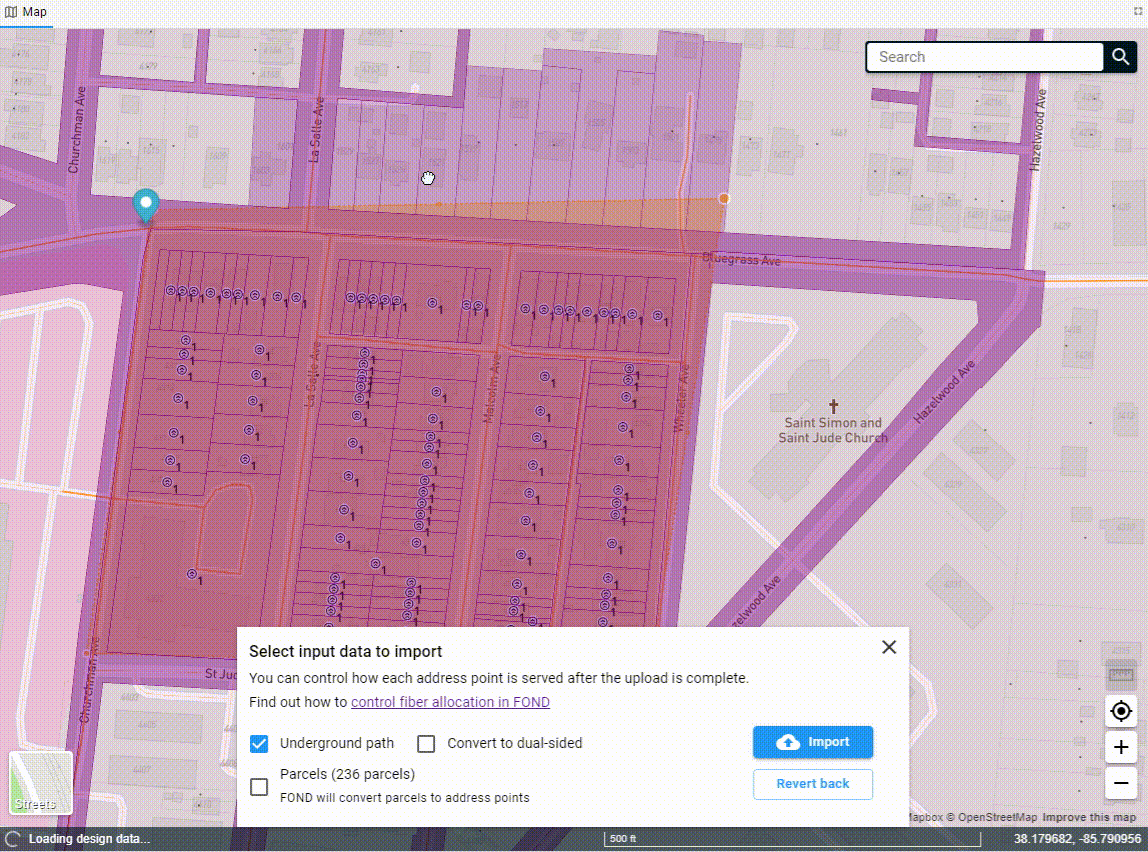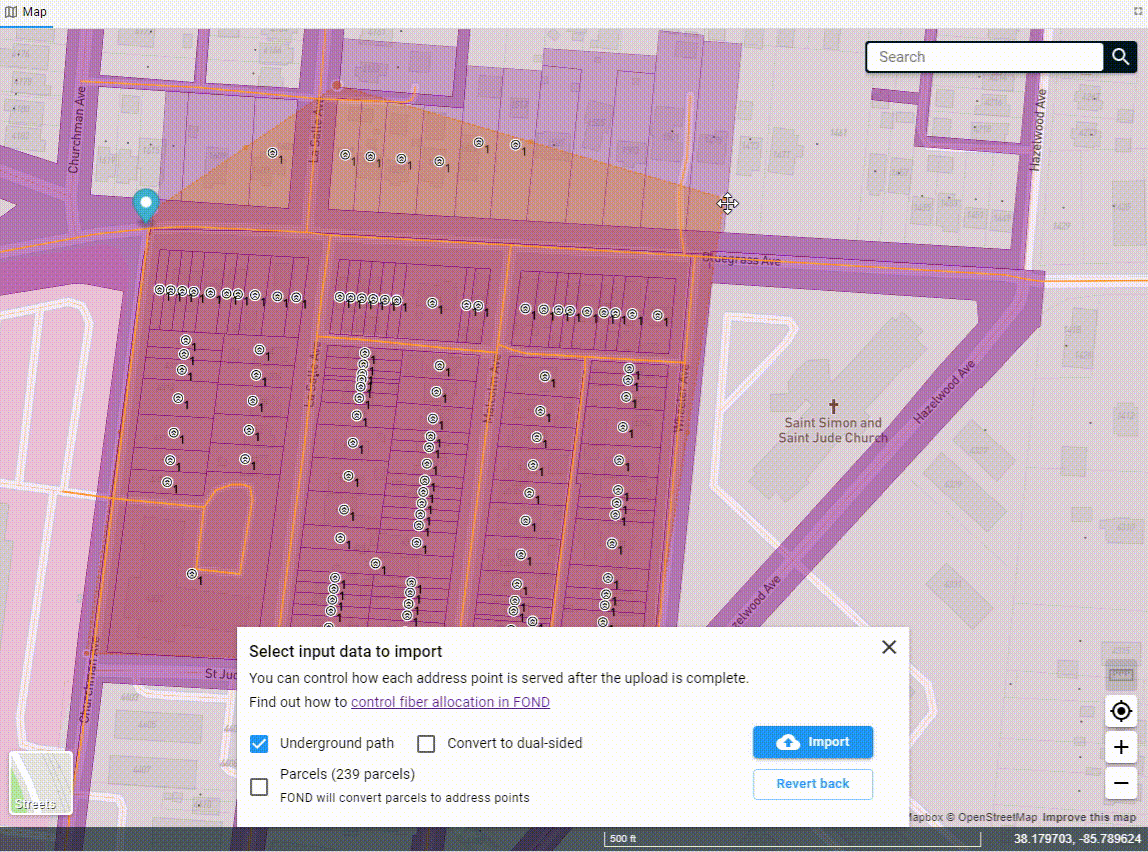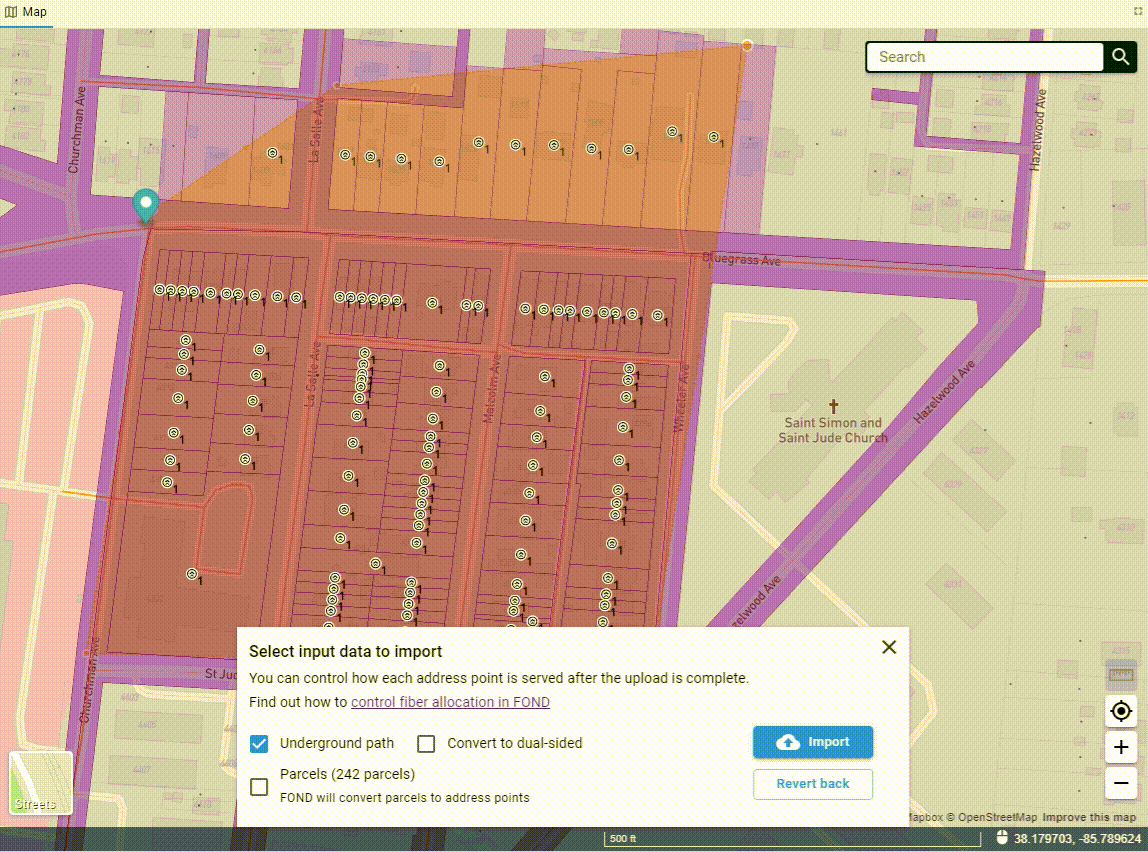
Uploading a polygon
You may upload an area select polygon rather than drawing one in FOND.
Using more than one polygon
You can use one polygon to area select address data, and another polygon to area select street data. This can be helpful when your addresses need to be contained to precise but disjoint areas, and your underground network needs to adequately connect them together.
Data limitations
Please refer to FOND Data Restrictions for information on data limits, such as the maximum area of an area select polygon and the maximum number of addresses that can be present in a project.